Match the following terms with the correct definition
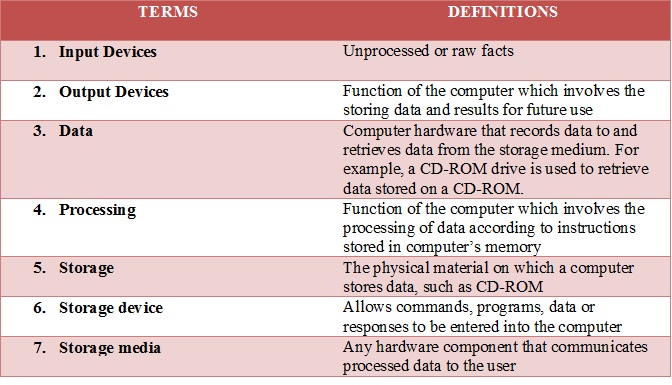
Types of Input Devices
- Manual Input devices-These are used by people to enter data by hand. Manual input devices require humans to do most of the work needed to get data into the system.
- Automated/Source Data Entry devices-Methods of capturing and entering data directly into the computer without any need for human intervention. (Direct input devices do not require much human interaction to get their data into a computer system). Sometimes called direct data entry, or DDE for short. Used when very large amounts of data need to be input quickly and accurately.
Manual input devices
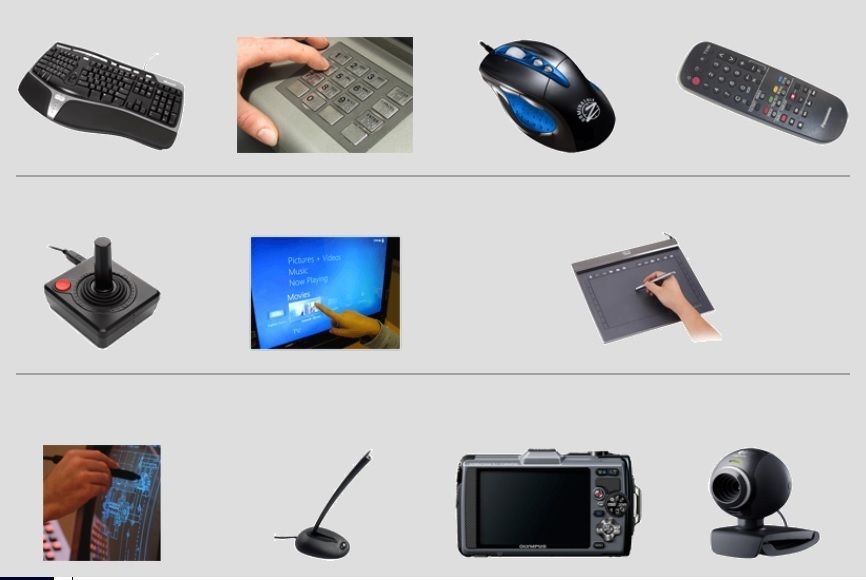

Automated/Source Data Entry Devices

Manual Devices
Keyboard
- The keyboard is the most common type of input device. This way of arranging the keys is called QWERTY because of the order that the keys appear in on the first row of letters.
- Uses of a Keyboard-used to input data into applications. Example entering text into word processing application like Microsoft Word and entering numbers into spreadsheet application like Microsoft Excel
Numeric Keypads
- These are used for entering numbers into a computer system (‘Numeric’ means number. Some numeric keypads allow the user to enter simple text and symbols.
- Uses of Numeric Keypad:
- ATM (Automatic teller Machines)-enter Personal Identification Numbers (PIN) into an ATM to allow us to get cash as well as keying in how much money we need from the ATM.
- Telephones- use to enter phone numbers
- Chip and Pin devices-use to enter PIN numbers and payment amounts when buying goods and paying for services
Pointing devices
- A mouse is a pointing device. It is the next most common type of input device after the keyboard. Touch pads and trackballs are also types of pointing device. They are often used instead of a mouse on portable computers.
- Mouse: Pieces of hardware that are used to control a pointer (cursor) on a screen
- Touchpad: used as replacement to a mouse in many laptops. Users lightly brush their finger over the touchpad in order to control a pointer
- Trackball: similar to the mouse but the ball is on the top of the device instead of the bottom. Screen pointer are controlled by rotating the large ball with your hand
- Uses of Mice, Touchpad and trackball:
- Opening, closing, maximizing and minimizing programs and files
- Moving, grouping and deleting files
- Controlling a pointer on screen to select icons or move around the page
- Editing images in terms of size and position on the screen
Remote Control
- Used to control other devices using infra-red signals
- Uses of Remote Controls:
- Home entertainment systems eg. Hi-Fi systems (music centers), DVD/Blu-ray players, satellite systems, some overhead projectors
- In industries to operate machinery that might be too dangerous to get near to, e.g. cranes with heavy loads, activating explosives in demolition, operating robot arms in hazardous chemical plants
Joystick
- The main use of a joystick is to play computer games by controlling the way that something moves on the screen.
- Joysticks can be used to control movement from side-to-side, up-and-down and diagonally.
- A joystick will also always have at least one button on it which can be used to make something happen like making a character in a game jump or fire a gun.
- Uses of Joysticks: control characters or objects in video games, control industrial machinery e.g. cranes and they are used in simulators-flight simulators for trainee pilots to control the simulated plane.
Touch screen
- A touch screen can detect exactly where on its surface it has been touched.
- Touch screens are used in a lot of fast food chains and restaurants because they are easy to keep clean and re-program if changes need to be made to the menu.
- Uses:
- Mobile phones and PDA (Personal Digital Assistant) uses touch screens as a way of saving space
- Public information systems at airports or tourist information offices
- Interactive whiteboards
- On-screen multiple choice tests (like driving theory tests)
Graphics Tablet
- A graphics tablet consists of a flat surface and a pen, or stylus, which can be used to produce freehand drawings or trace around shapes. When the special pen touches the surface of the graphics tablet data about its position is sent to the computer. This data is used to produce on the screen an exact copy of what is being drawn on the surface of the graphics tablet.
- Uses:
- Allow designers to produce digital images much more accurately than if they were using a mouse
Light Pen
- A light pen is a small ‘pen-shaped’ wand, which contains light sensors. It is used to choose objects or commands on the screen either by pressing it against the surface of the screen or by pressing a small switch on its side.
- A signal is sent to the computer, which then works out the light pen’s exact location on the screen. The advantage of a light pen is that it doesn’t need a special screen or screen coating.
- Uses:
- for selecting objects on a CRT (Cathode Ray tube) screen
- Used for directly drawing onto a CRT screen
Microphone
- A microphone is used to input sound into a computer system. Microphones are often used for voice recognition systems which convert sounds made by a user into commands that the computer can carry out.
- Systems like this are very useful for people who can’t use ordinary input devices such as the mouse and keyboard. As computers become more powerful in the future, voice recognition will be a much more common input method for all computer users.
- Uses:
- Used to input sounds/speech for use in a range of applications e.g. narration (spoken words) in presentations or in web sites, voice-overs in movies, Speaking over the internet using VoIP(Voice over Internet Protocol) – Skype and conducting videoconferencing (business meetings online)
- Used in voice recognition software e.g. converting speech into text, issuing commands-‘starting the engine’
- Hand-free mobile phones use a microphone to allow people to hold conversations without using their hands
- Used along with headphones in gaming so that gamers can talk to each other
Digital Camera
- A digital camera can store many more pictures than an ordinary camera.
- Pictures taken using a digital camera are stored inside its memory and can be transferred to a computer by connecting the camera to it. A digital camera takes pictures by converting the light passing through the lens at the front into a digital image.
- Most digital cameras also allow for short, high- quality video clips to be produced.
Web Cameras (Webcam)
- Web cameras are similar to digital camera in their function but they are directly connected to a computer and do not have memory storage.
- Web camera can capture both digital images and video. Images/ video are sent directly to the computer where they can be stored and used.
- Uses:
- to conduct face-face conversations with and family online over VoIP applications such as Skype
- to hold video-conferencing meetings over the internet
- Can capture image and video content for presentations, web sites and even YouTube content
- Some use webcams as a cheap alterative to security cameras
- Used to allow drivers to view the traffic conditions on roads
Automated/Source Data Entry Devices
Scanner
- A scanner can be used to input pictures and text into a computer or enter information on paper (hard copies) into a computer. There are two main types of scanner; Hand-held and Flat-bed.
- Uses of scanners:
- Old photos and important documents can be scanned into the computer. This means you still have a copy if the original is damaged or lost.
Magnetic stripe readers
- A magnetic stripe is a thin band of magnetic tape
- Often on the back of a credit or debit card, identity cards and electronic key cards in hotels and businesses
- Magnetic stripes can hold only a small amount of data and are quite easy to forge In the next few years magnetic stripes will be replaced with smart cards which store much more data on a small microchip built into the surface of the card
- The strips on the cards holds information such as bank account number, name of card holder, expiry date of membership etc.
- Data contained on the card’s stripe is read by pulling the card through the magnetic stripe reader –this is known as ‘swiping’
- Uses: ATM use these readers to process the information on bank cards, EFTPOS (Electronic Funds Transfer Point of Sale) use the readers to transfer customer’s money from their bank accounts when they purchase goods in stores and hotel rooms sometimes use magnetic stripe readers in place of door keys.
Chip and Pin Reader
- These allow people to pay for goods and services electronically at EFTPOS terminals.
- The chip and pin reader works by inserting a bank/credit card into a slot and then entering a PIN. If the correct PIN is entered, the cost of goods/services will be taken from the card holder’s bank and transferred to the companies (restaurant, store etc.)
- Uses: Used to make secure payments for goods/services in places such as: supermarkets, restaurants, cafes, buying petrol etc.
Bar Code Reader/Scanner
- A bar code is a set of lines of different thicknesses that represent a number
- Most products in shops have bar codes on them.
- Bar codes represent a code number for a product. It holds information about each product including product ID number, manufacturer and country of origin. Prices are not stored in the barcode.
- Bar Code Readers are used to input data from bar codes.
- Bar code readers work by shining a beam of light on the lines that make up the bar code and detecting the amount of light that is reflected back.
- Once a barcode has been scanned, a computer can read the information stored on the barcode and access details about the product that are stored in a database.
- Uses:
- in supermarket, stores and warehouses where goods are marked with a barcode
- Used in libraries to scan in library cards and read ISBN numbers on books to find out which ones are on loan.
- They are used in keeping track of packages that are being delivered to different locations
- Used in organizing luggage in airports (helps ensure that luggage is loaded onto the correct plane.
Optical Mark Reader/Recognition (OMR)
- OMR uses an input device called an optical mark reader to detect marks made in certain places on specially printed forms.
- A fast input method, used where large amounts of data need to be input quickly.
- Used to input data from things like answer sheets for multiple choice exams and registration forms in schools and also National Lottery forms
Magnetic Ink Character Recognition (MICR)
- MICR uses an input device called a magnetic ink character reader to input characters that have been printed in special magnetic ink
- Banks use MICR to process cheques, because it is very secure
- The equipment needed to print and read characters in magnetic ink is very expensive.
- MICR can be used to read the following information-customer account number, branch number and cheque number
Optical Character Reader/Recognition (OCR)
- OCR is the use of an ordinary scanner and special software to convert text in a scanned image into a format that can be edited by word processing software
- Text must be printed or written very clearly
- OCR depends on the shape of the marks whereas OMR depends on the position of the marks
- Used for the reading of typed postcodes, used in the processing of passports and identity cards and to digitize books
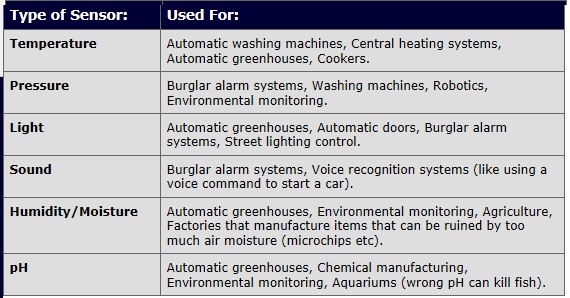
Sensors
- Sensors are used to detect physical quantities outside a computer such as temperature, pressure and light
- To be able to process input from sensors a device called an analogue-to-digital converter must be connected between the computer and the sensors.
- This device converts signals from sensors into digital data that the computer can process.
- Used in monitoring and control applications
Game
http://www.teach-ict.com/gcse_new/computer%20systems/input_devices/quiz/walkplank_input.htm
End of Lesson Activity
Click on the link: Input Device End of Lesson Activity Grade 8
Answers
References
https://revisionworld.com/gcse-revision/ict/hardware/manual-input-peripherals-or-devices
http://www.ictlounge.com/html/manual_input_devices.htm
YouTube-https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=HQOxWiuOcps
Good night mrs dacosta walker I am from 8nine class and I do not see lesson 4 so can you please check it out? Thank you.
LikeLike
Its up now
LikeLike
Miss i dont understand please can u explain to please 8-8 and u don’t have to answer mi online oj miss
LikeLike
See your teacher.
LikeLike